Traditionally, the communication between electric vehicles (EVs) and EV charger is governed by two standards: DIN 70121 and ISO 15118. DIN 70121 is more prevalent in this field because it was released earlier than the current version of ISO 15118-2. However, ISO 15118-2 boasts more comprehensive functions, including “Plug and Charge” (plug-and-play charging), encryption, and digital certificates.
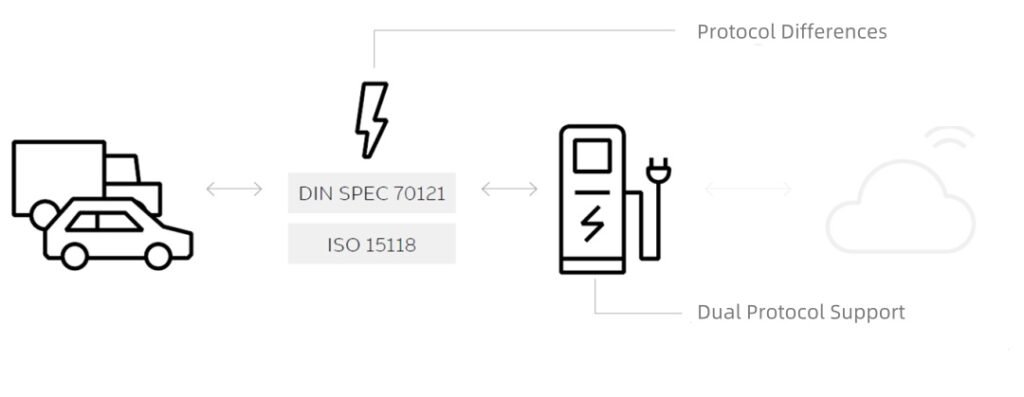
These protocols are not interoperable, which means that electric vehicles (EVs) supporting only DIN 70121 cannot be charged by EV charger that support only ISO 15118, and vice versa. Fortunately, many EV charger are compatible with both standards. Therefore, when a vehicle is plugged into one of these charger, it will “inform” the charger of the protocol (literally “language” in the original text, adjusted to “protocol” for technical accuracy) it supports, and the charger can respond accordingly. However, although many EV charger support ISO 15118, a large number of EVs do not. These automakers need time to implement the ISO 15118-2 protocol.
DIN 70121 Protocol
This German standard defines the communication between DC charger and electric vehicles (EVs), and incorporates technical specifications based on the early version of ISO 15118-2.
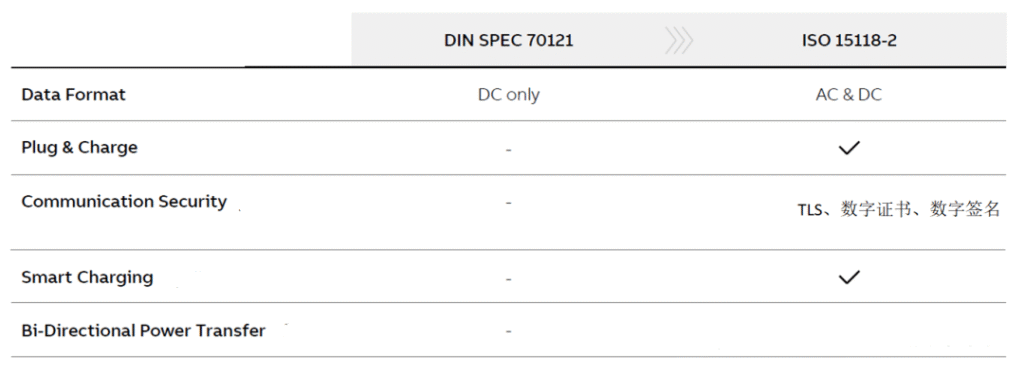
The release of DIN 70121 has provided standardized communication requirements for electric vehicles (EVs). DIN 70121 remains prevalent today, yet it has several limitations, including the lack of support for alternating current (AC) charging, Transport Layer Security (TLS), digital certificates, “Plug and Charge” functionality, and digital signatures. The DIN 70121 protocol is simpler and easier to implement, which partly explains why it is still common in the market and why the transition to ISO 15118-2 is proceeding more slowly than expected.
ISO 15118 Protocol
This is a standard series that defines the communication requirements for the Electric Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) interface.
ISO 15118 consists of multiple parts, each addressing different aspects of communication and representing improvements over DIN 70121. Key features such as “Plug and Charge” and Transport Layer Security (TLS) enable a more secure charging experience. Specifically, Plug and Charge facilitates the secure exchange of certificates between the electric vehicle (EV) and the charging pile, allowing the charging pile to authenticate the vehicle and automatically authorize payments without the need for swiping a card. This simplifies the process for EV drivers, who only need to plug in the charging cable to automatically initiate a charging session.
To ensure consistent charging experiences across different manufacturers, the ISO 15118 standard series includes conformance testing, which incorporates pass-or-fail criteria to verify whether an implementation complies with the standard.
